Fluids
Overview
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics and engineering concerned with the behavior of fluids (liquids and gases) at rest and in motion. It provides the theoretical foundation for understanding and predicting fluid flow, pressure distribution, drag forces, and heat transfer in countless engineering applications—from pipelines and HVAC systems to aircraft design and chemical processing.
At its core, fluid mechanics combines conservation principles (mass, momentum, and energy) with empirical correlations to solve practical problems. These problems span multiple scales: from predicting atmospheric density at 80 km altitude, to sizing industrial control valves, to calculating pressure drop in miles of natural gas pipeline.
Atmospheric modeling tools implement the US Standard Atmosphere 1976 and the NRLMSISE-00 model to compute temperature, pressure, and density as functions of altitude. These are essential for aerospace applications, satellite drag calculations, and meteorological studies.
Compressible flow calculations handle gas flows where density changes significantly, using equations derived from thermodynamics and the ideal gas law. The tools include isentropic relations, stagnation properties, critical flow conditions, and empirical pipeline formulas (Panhandle A/B, Weymouth, Fritzsche) widely used in the natural gas industry for long-distance transmission.
Control valve sizing and analysis follows the IEC 60534 international standard for liquid and gas service. The tools compute flow coefficients (Cv, Kv, Av), predict choked flow conditions, evaluate cavitation risk, and estimate valve noise levels—critical for safe and efficient process control in chemical plants and refineries.
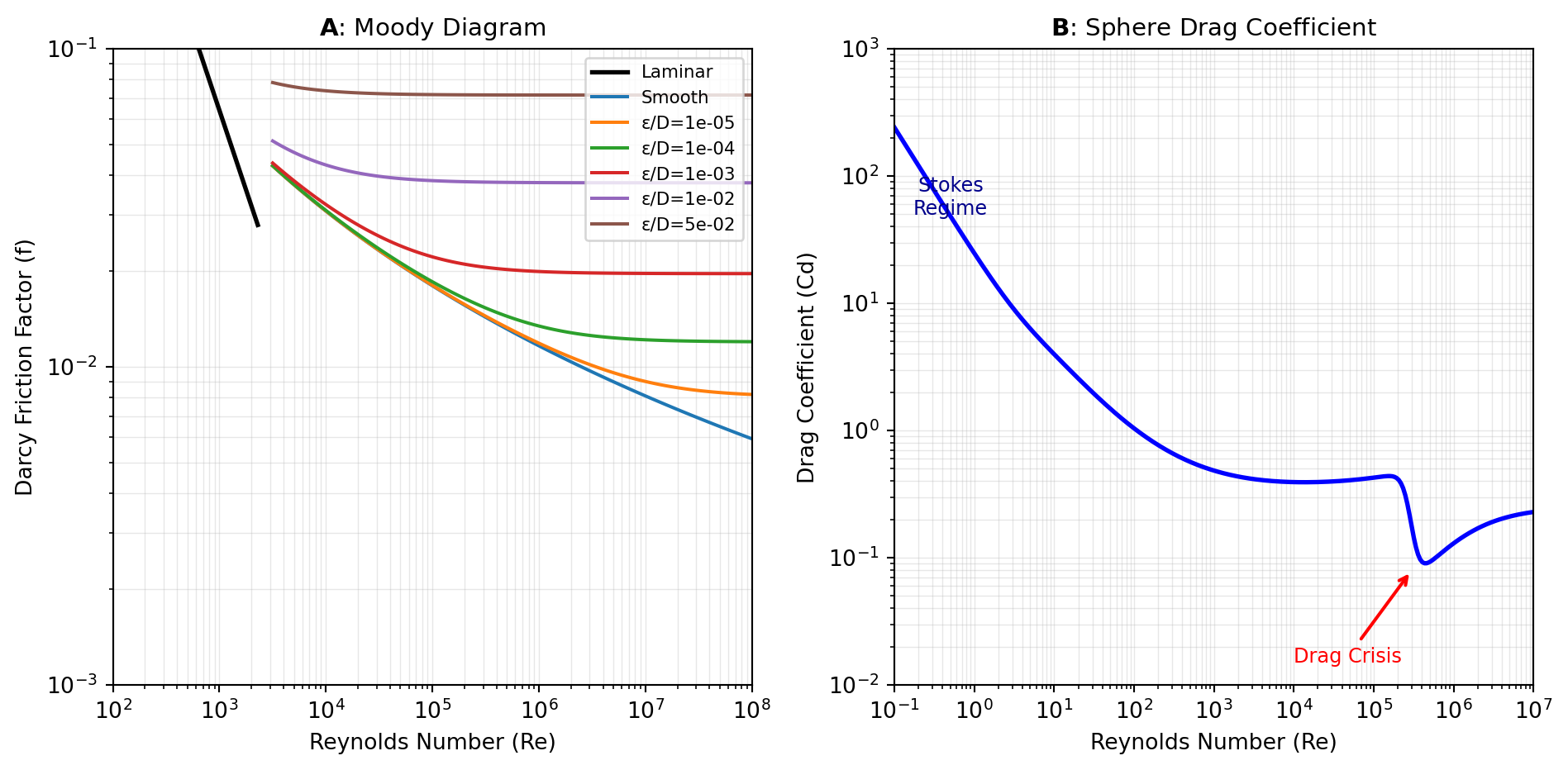
Dimensionless numbers characterize fluid behavior and enable scaling between different systems. Key numbers include Reynolds (inertial vs. viscous forces), Froude (inertial vs. gravitational forces), Bond (gravitational vs. surface tension forces), and many others used in heat transfer, two-phase flow, and boundary layer analysis.
Drag analysis provides correlations for the drag coefficient of spheres across the full Reynolds number range, from Stokes flow (Re < 1) to the drag crisis regime (Re > 10⁵). Multiple empirical correlations (Morrison, Clift, Haider-Levenspiel, etc.) offer varying accuracy and complexity for settling calculations, particle tracking, and multiphase flow modeling.
Pipe friction and fittings implement the Darcy-Weisbach equation and the Colebrook equation (solved exactly or via fast approximations) to calculate pressure drop in pipes. Additional tools compute loss coefficients (K-factors) for bends, expansions, contractions, valves, and other fittings based on industry-standard correlations from Crane TP-410 and other references.
All implementations leverage the fluids library, a comprehensive open-source Python package developed by Caleb Bell that provides validated, unit-tested functions for fluid mechanics calculations. The library wraps algorithms from authoritative sources including ASHRAE handbooks, ISO standards, and peer-reviewed literature.

Atmosphere
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| AIRMASS | Calculate the mass of air per square meter in the atmosphere along a given angle using a density profile. |
| ATMOS_NRLMSISE00 | Compute temperature, density, and pressure using the NRLMSISE-00 atmospheric model. |
| ATMOSPHERE_1976 | Calculate standard atmospheric properties at a given altitude using the US Standard Atmosphere 1976 model. |
Compressible
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| FRITZSCHE_FLOW | Calculate gas flow rate using the Fritzsche formula. |
| IGT_FLOW | Calculate gas flow rate using the IGT (Institute of Gas Technology) formula. |
| IS_CHOKED_FLOW | Determine if a flow is choked (critical) based on pressure ratio. |
| ISENTROPIC_EFF | Convert between isentropic and polytropic efficiency for compression. |
| ISENTROPIC_T_RISE | Calculate the temperature rise for isentropic compression or expansion. |
| ISENTROPIC_WORK | Calculate work of compression or expansion for a gas in an isentropic process. |
| ISOTHERMAL_GAS | Calculate mass flow rate for isothermal compressible gas flow in a pipe. |
| ISOTHERMAL_WORK | Calculate work of compression or expansion for a gas in an isothermal process. |
| MULLER_FLOW | Calculate gas flow rate using the Muller formula. |
| P_CRITICAL_FLOW | Calculate critical flow pressure for a fluid at Mach 1. |
| P_STAGNATION | Calculate stagnation pressure from static conditions. |
| PANHANDLE_A | Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Panhandle A formula. |
| PANHANDLE_B | Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Panhandle B formula. |
| POLYTROPIC_EXP | Calculate polytropic exponent or polytropic efficiency for compression. |
| STAGNATION_ENERGY | Calculate the increase in enthalpy due to fluid velocity. |
| T_CRITICAL_FLOW | Calculate critical flow temperature for a fluid at Mach 1. |
| T_STAG_IDEAL | Calculate ideal stagnation temperature from velocity and heat capacity. |
| T_STAGNATION | Calculate stagnation temperature from pressure ratio. |
| WEYMOUTH_FLOW | Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Weymouth formula. |
Control Valve
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| CV_CAV_INDEX | Calculates the cavitation index of a control valve. |
| CV_CHAR_EQ_PERC | Calculates the flow coefficient characteristic for an equal percentage control valve. |
| CV_CHAR_LINEAR | Calculates the flow coefficient characteristic for a linear control valve. |
| CV_CHAR_QUICK_OP | Calculates the flow coefficient characteristic for a quick opening control valve. |
| CV_CHOKE_PRESS_GAS | Calculates the pressure at which choked flow occurs in a gas control valve. |
| CV_CHOKE_PRESS_LIQ | Calculates the pressure at which choked flow occurs in a liquid control valve. |
| CV_CONVERT_COEFF | Converts between different flow coefficient scales (Kv, Cv, Av). |
| CV_NOISE_GAS_2011 | Calculate the A-weighted sound pressure level for gas flow through a control valve per IEC 60534-8-3 (2011). |
| CV_NOISE_LIQ_2015 | Calculates the sound made by a liquid flowing through a control valve according to the standard IEC 60534-8-4 (2015) using fluids.control_valve.control_valve_noise_l_2015. |
| FF_CRIT_PRESS_L | Calculates FF, the liquid critical pressure ratio factor, for use in IEC 60534 liquid valve sizing calculations using fluids.control_valve.FF_critical_pressure_ratio_l. |
| IS_CHOKED_GAS | Determines if a gas flow in a control valve is choked (critical) or not according to IEC 60534. |
| IS_CHOKED_LIQ | Determines if a liquid flow in a control valve is choked (critical) or not according to IEC 60534. |
| LOSS_COEFF_PIPING | Calculates the sum of loss coefficients for reducers/expanders around a control valve. |
| REYNOLDS_FACTOR | Calculates the Reynolds number factor FR for a valve according to IEC 60534. |
| REYNOLDS_VALVE | Calculates the Reynolds number of a control valve according to IEC 60534. |
| SIZE_CV_GAS | Calculates flow coefficient of a control valve passing a gas according to IEC 60534 using fluids.control_valve.size_control_valve_g. |
| SIZE_CV_LIQUID | Calculates the flow coefficient (Kv) of a control valve passing a liquid according to IEC 60534. |
Dimensionless
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| ARCHIMEDES | Calculate the Archimedes number (Ar) for a fluid and particle. |
| BEJAN | Compute the Bejan number (length-based or permeability-based). |
| BIOT | Calculate the Biot number for heat transfer. |
| BOILING | Calculate the Boiling number (Bg), a dimensionless number for boiling heat transfer. |
| BOND | Calculate the Bond number (Bo), also known as the Eötvös number (Eo). |
| CAPILLARY | Calculate the Capillary number (Ca) for a fluid system using fluids.core.Capillary. |
| CAVITATION | Calculate the Cavitation number (Ca) for a flowing fluid. |
| CONFINEMENT | Calculate the Confinement number (Co) for two-phase flow in a channel. |
| DEAN | Calculate the Dean number (De) for flow in a curved pipe or channel. |
| DRAG | Calculate the drag coefficient (dimensionless) for an object in a fluid. |
| ECKERT | Calculate the Eckert number using fluids.core.Eckert. |
| EULER | Calculate the Euler number (Eu) for a fluid flow. |
| FOURIER_HEAT | Calculate the Fourier number for heat transfer. |
| FOURIER_MASS | Calculate the Fourier number for mass transfer (Fo). |
| FROUDE | Calculate the Froude number (Fr) for a given velocity, length, and gravity. |
| FROUDE_DENSIMETRIC | Calculate the densimetric Froude number. |
| GRAETZ_HEAT | Calculate the Graetz number. |
| GRASHOF | Calculate the Grashof number. |
| HAGEN | Calculate the Hagen number. |
| JAKOB | Calculate the Jakob number for boiling fluid. |
| KNUDSEN | Calculate the Knudsen number. |
| LEWIS | Calculate the Lewis number. |
| MACH | Calculate the Mach number. |
| MORTON | Calculate the Morton number. |
| NUSSELT | Calculate the Nusselt number. |
| OHNESORGE | Calculate the Ohnesorge number. |
| PECLET_HEAT | Calculate the Peclet number for heat transfer. |
| PECLET_MASS | Calculate the Peclet number for mass transfer. |
| POWER_NUMBER | Calculate the Power number for an agitator. |
| PRANDTL | Calculate the Prandtl number. |
| RAYLEIGH | Calculate the Rayleigh number. |
| RELATIVE_ROUGHNESS | Calculate the relative roughness. |
| REYNOLDS | Calculate the Reynolds number. |
| SCHMIDT | Calculate the Schmidt number. |
| SHERWOOD | Calculate the Sherwood number. |
| STANTON | Calculate the Stanton number. |
| STOKES_NUMBER | Calculate the Stokes number. |
| STROUHAL | Calculate the Strouhal number. |
| SURATMAN | Calculate the Suratman number. |
| WEBER | Calculate the Weber number. |
Drag
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| CD_ALMEDEIJ | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Almedeij correlation. |
| CD_BARATI | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Barati correlation. |
| CD_BARATI_HIGH | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Barati high-Re correlation (valid to Re=1E6). |
| CD_CEYLAN | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Ceylan correlation. |
| CD_CHENG | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Cheng correlation. |
| CD_CLIFT | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Clift correlation. |
| CD_CLIFT_GAUVIN | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Clift-Gauvin correlation. |
| CD_ENGELUND | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Engelund-Hansen correlation. |
| CD_FLEMMER_BANKS | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Flemmer-Banks correlation. |
| CD_GRAF | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Graf correlation. |
| CD_HAIDER_LEV | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Haider-Levenspiel correlation. |
| CD_KHAN_RICH | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Khan-Richardson correlation. |
| CD_MIKHAILOV | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Mikhailov-Freire correlation. |
| CD_MORRISON | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Morrison correlation. |
| CD_MORSI_ALEX | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Morsi-Alexander correlation. |
| CD_ROUSE | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Rouse correlation. |
| CD_SONG_XU | Calculate drag coefficient of a particle using the Song-Xu correlation for spherical and non-spherical particles. |
| CD_STOKES | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using Stokes law (Cd = 24/Re). |
| CD_SWAMEE_OJHA | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Swamee-Ojha correlation. |
| CD_TERFOUS | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Terfous correlation. |
| CD_YEN | Calculate drag coefficient of a sphere using the Yen correlation. |
| DRAG_SPHERE | Calculate the drag coefficient of a sphere using various correlations based on Reynolds number. |
| SPHERE_FALL_DIST | Calculate distance traveled by a falling sphere after a given time. |
| SPHERE_VEL_AT_T | Calculate the velocity of a falling sphere after a given time. |
| TIME_V_TERMINAL | Calculate time for a particle in Stokes regime to reach terminal velocity. |
| V_TERMINAL | Calculate terminal velocity of a falling sphere using drag coefficient correlations. |
Filters
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| RND_EDGE_GRILL | Calculate the loss coefficient for a rounded edge grill or perforated plate. |
| RND_EDGE_MESH | Calculate the loss coefficient for a round edged open net or screen mesh. |
| RND_EDGE_SCREEN | Calculate the loss coefficient for a round edged wire screen or bar screen. |
| SQ_EDGE_GRILL | Calculate the loss coefficient for a square edged grill or perforated plate. |
| SQ_EDGE_SCREEN | Calculate the loss coefficient for a square edged wire screen, bar screen, or perforated plate. |
Fittings
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| BEND_MITER | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a single-joint miter bend in a pipe. |
| BEND_ROUNDED | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a rounded pipe bend (elbow) using various methods. |
| CONTRACTION_ROUND | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a rounded pipe contraction (reducer). |
| CONTRACTION_SHARP | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a sharp edged pipe contraction (reducer). |
| CV_TO_K | Convert imperial valve flow coefficient (Cv) to loss coefficient (K). |
| DIFFUSER_CONICAL | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a conical pipe expansion (diffuser). |
| DIFFUSER_SHARP | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a sudden pipe expansion (diffuser). |
| ENTRANCE_ANGLED | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for an angled sharp entrance to a pipe flush with a reservoir wall. |
| ENTRANCE_BEVELED | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a beveled or chamfered entrance to a pipe flush with a reservoir wall. |
| ENTRANCE_ROUNDED | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a rounded entrance to a pipe flush with a reservoir wall. |
| ENTRANCE_SHARP | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a sharp entrance to a pipe flush with a reservoir wall. |
| EXIT_NORMAL | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a normal pipe exit discharging into a reservoir. |
| HELIX | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a helical coil pipe section. |
| K_BALL_VALVE | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a ball valve using the Crane method. |
| K_BUTTERFLY_VALVE | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a butterfly valve using the Crane method. |
| K_GATE_VALVE | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a gate valve using the Crane method. |
| K_GLOBE_VALVE | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a globe valve using the Crane method. |
| K_SWING_CHECK_VALVE | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a swing check valve using the Crane method. |
| K_TO_CV | Convert loss coefficient (K) to imperial valve flow coefficient (Cv). |
| K_TO_KV | Convert loss coefficient (K) to metric valve flow coefficient (Kv). |
| KV_TO_K | Convert metric valve flow coefficient (Kv) to loss coefficient (K). |
| SPIRAL | Calculate the loss coefficient (K) for a spiral coil pipe section. |
Flow Meter
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| DIFF_PRESS_BETA | Calculate the beta ratio (diameter ratio) for a differential pressure flow meter. |
| DIFF_PRESS_C_EPS | Calculate discharge coefficient and expansibility factor for differential pressure flow meters. |
| DIFF_PRESS_DP | Calculate non-recoverable pressure drop across a differential pressure flow meter. |
| FLOW_METER_DISCH | Calculate mass flow rate through a differential pressure flow meter based on measured pressures and meter geometry. |
| ORIFICE_DISCHARGE_C | Calculate the discharge coefficient for an orifice plate using the Reader-Harris-Gallagher correlation (ISO 5167 standard). |
| ORIFICE_EXPAND | Calculate the expansibility factor for an orifice plate based on geometry and pressure conditions. |
| ORIFICE_PRESS_DROP | Calculate non-recoverable pressure drop across an orifice plate based on geometry and discharge coefficient. |
Friction
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| BLASIUS | Calculates Darcy friction factor for turbulent flow in smooth pipes using the Blasius correlation. |
| CHURCHILL | Calculate Darcy friction factor using the Churchill (1977) universal equation for all flow regimes. |
| CLAMOND | Calculate Darcy friction factor using Clamond’s high-precision solution accurate to nearly machine precision. |
| COLEBROOK | Calculate Darcy friction factor using exact solution to the Colebrook equation. |
| DP_GRAV | Calculate gravitational pressure drop component for single-phase flow in inclined pipes. |
| FF_CURVED | Calculate friction factor for fluid flowing in a curved pipe or helical coil, supporting both laminar and turbulent regimes. |
| FP_MARTIN | Calculate Darcy friction factor for single-phase flow in Chevron-style plate heat exchangers using Martin (1999) correlation. |
| FP_MULEY_MANGLIK | Calculate Darcy friction factor for single-phase flow in Chevron-style plate heat exchangers using Muley-Manglik correlation. |
| FRICTION_FACTOR | Calculate the Darcy friction factor for fluid flow in a pipe using various correlations, automatically selecting appropriate method based on Reynolds number and relative roughness. |
| FRICTION_LAMINAR | Calculate the Darcy friction factor for laminar flow using the theoretical solution fd = 64/Re. |
| FT_CRANE | Calculate the Crane fully turbulent Darcy friction factor for flow in commercial pipe. |
| HAALAND | Calculate Darcy friction factor using the Haaland (1983) approximation. |
| HELICAL_RE_CRIT | Calculate the transition Reynolds number for fluid flowing in a curved or helical pipe between laminar and turbulent flow. |
| MOODY | Calculate Darcy friction factor using the Moody (1947) correlation. |
| ONE_PHASE_DP | Calculate single-phase pressure drop in a pipe using the Darcy-Weisbach equation. |
| SWAMEE_JAIN | Calculate Darcy friction factor using the Swamee-Jain (1976) equation. |
| TRANS_FACTOR | Convert between Darcy friction factor and transmission factor for compressible gas pipeline flow. |
| VON_KARMAN | Calculate Darcy friction factor for rough pipes at infinite Reynolds number from the von Karman equation. |