Interpolation
Overview
Interpolation is the mathematical process of constructing new data points within a discrete set of known data points. At its core, interpolation assumes that the true underlying relationship between variables can be approximated by connecting existing observations with some smooth or structured function. This makes it fundamental to data analysis, scientific computing, computer graphics, and engineering applications.
The basic problem is straightforward: given a set of points (x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), \ldots, (x_n, y_n), find a function f(x) such that f(x_i) = y_i for all i. The function f can then be used to estimate values at positions not in the original dataset. Interpolation differs from curve fitting in that it passes exactly through the data points, whereas fitting methods (like least squares) allow deviations to reduce the impact of noise. It also differs from extrapolation, which estimates values outside the range of known data points—a much riskier endeavor prone to larger errors.
Implementation: Interpolation tools are built on SciPy, which provides robust implementations of classical interpolation methods. The choice of interpolation method depends on the data’s characteristics, the required smoothness, computational efficiency, the dimensionality of the data, and whether the data has measurement noise.
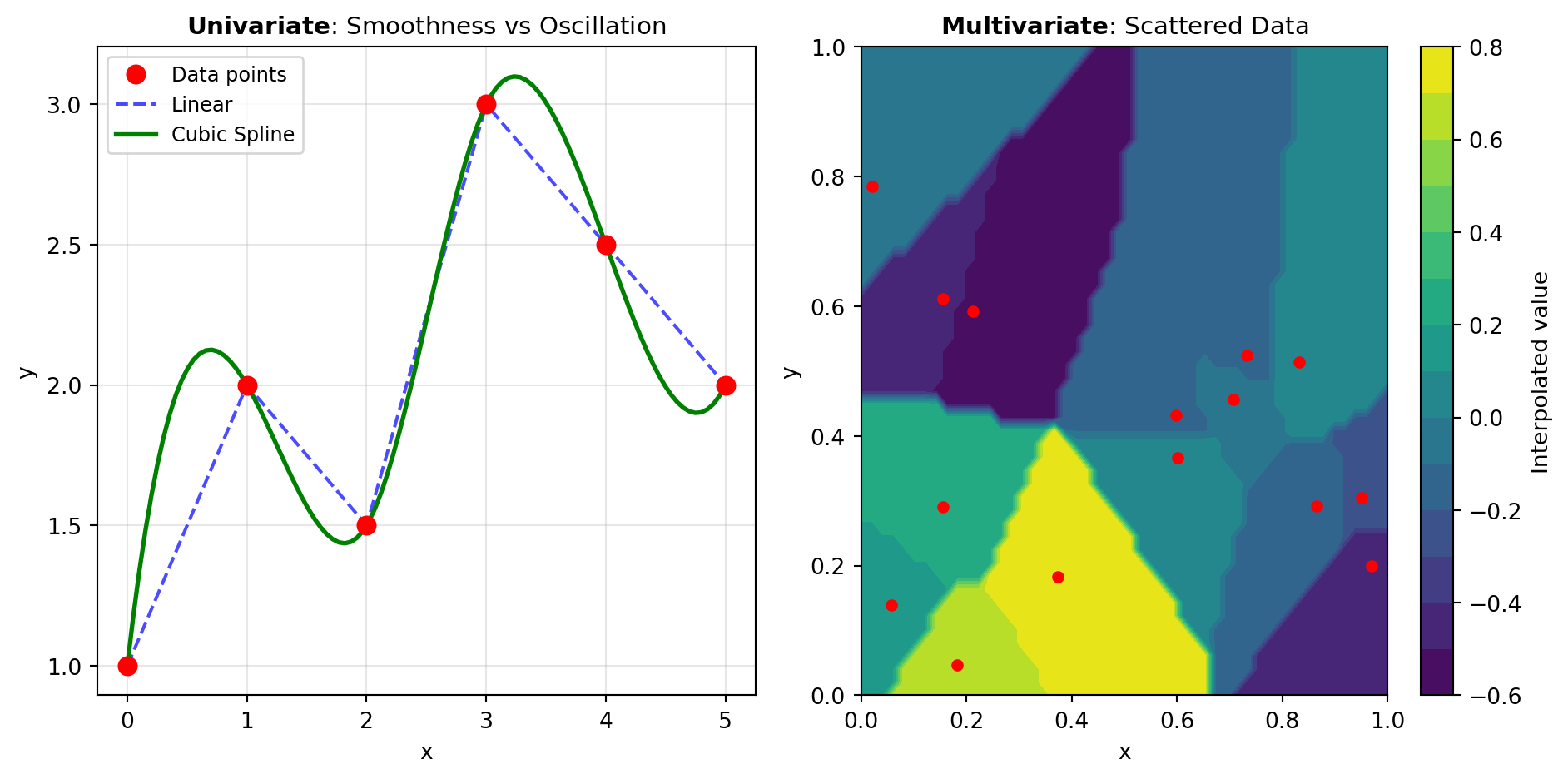
Univariate Interpolation: For one-dimensional data, univariate methods offer a spectrum of approaches. Simple methods like INTERP1D and CUBIC_SPLINE work well for ordered data. More sophisticated techniques like AKIMA_INTERP and PCHIP_INTERPOLATE preserve monotonicity and avoid oscillations, making them ideal for physical quantities that should not over-oscillate. Polynomial-based approaches like LAGRANGE_INTERP and BARYCENTRIC_INTERP provide explicit polynomial interpolation, while HERMITE_SPLINE matches both function values and derivatives at points. KROGH_INTERPOLATE offers another polynomial approach with numerical stability improvements.
Spline Interpolation: Splines are piecewise polynomial functions that offer exceptional flexibility and smoothness. MAKE_INTERP_SPLINE computes B-splines that pass through all data points, while UNIVARIATE_SPLINE adds smoothing to handle noisy data. MAKE_LSQ_SPLINE performs least-squares fitting with B-splines, combining interpolation principles with noise robustness. INTERP_UV_SPLINE provides univariate spline interpolation with automatic smoothing. SMOOTH_SPLINE implements cubic smoothing splines that balance fitting data while controlling wiggles.
Multivariate Interpolation: Higher-dimensional data requires specialized approaches. LINEAR_ND_INTERP and NEAREST_ND_INTERP provide fast methods for N-dimensional data, with linear interpolation offering smoothness and nearest-neighbor providing robustness. GRID_INTERP and INTERPN handle regularly-gridded data efficiently in 2D and higher dimensions. For scattered (unstructured) data, GRIDDATA provides flexible interpolation using various methods, while RBF_INTERPOLATOR uses radial basis functions to interpolate smoothly in arbitrary dimensions.
Approximation Methods: Beyond standard interpolation, PADE offers rational function approximation, which can be more efficient than polynomials for certain types of functions, particularly those with singularities or asymptotic behavior.
Figure 1 illustrates the spectrum of interpolation methods across different data characteristics and dimensionalities.

Approximation
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| LAGRANGE_INTERP | Compute the Lagrange interpolating polynomial through a set of points. |
| PADE | Compute Pade rational approximation to a polynomial. |
Multivariate
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| GRID_INTERP | Interpolator on a regular grid in 2D. |
| GRIDDATA | Interpolate unstructured D-D data. |
| INTERPN | Multidimensional interpolation on regular grids (2D). |
| LINEAR_ND_INTERP | Piecewise linear interpolator in N > 1 dimensions. |
| NEAREST_ND_INTERP | Nearest neighbor interpolation in N > 1 dimensions. |
| RBF_INTERPOLATOR | Radial basis function interpolation in N dimensions. |
Splines
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| INTERP_UV_SPLINE | 1-D interpolating spline for data. |
| MAKE_INTERP_SPLINE | Compute interpolating B-spline and evaluate at new points. |
| MAKE_LSQ_SPLINE | Compute LSQ-based fitting B-spline. |
| SMOOTH_SPLINE | Smoothing cubic spline. |
| UNIVARIATE_SPLINE | 1-D smoothing spline fit to data. |
Univariate
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| AKIMA_INTERP | Akima 1D interpolation. |
| BARYCENTRIC_INTERP | Interpolating polynomial for a set of points using barycentric interpolation. |
| CUBIC_SPLINE | Cubic spline data interpolator. |
| HERMITE_SPLINE | Piecewise-cubic interpolator matching values and first derivatives. |
| INTERP1D | Interpolate a 1-D function. |
| KROGH_INTERPOLATE | Krogh polynomial interpolation. |
| PCHIP_INTERPOLATE | PCHIP 1-D monotonic cubic interpolation. |