Atmosphere
Overview
Atmospheric modeling is essential for aerospace engineering, satellite operations, meteorology, and environmental science. These tools provide computational methods to characterize the Earth’s atmosphere at different altitudes and conditions, addressing how temperature, pressure, density, and composition vary with altitude, latitude, time, and solar activity.
The atmosphere is a complex, dynamic system influenced by gravitational compression, solar radiation, geomagnetic activity, and seasonal variations. Accurate atmospheric models are critical for aircraft performance calculations, rocket trajectory analysis, satellite drag estimation, and atmospheric reentry simulations.
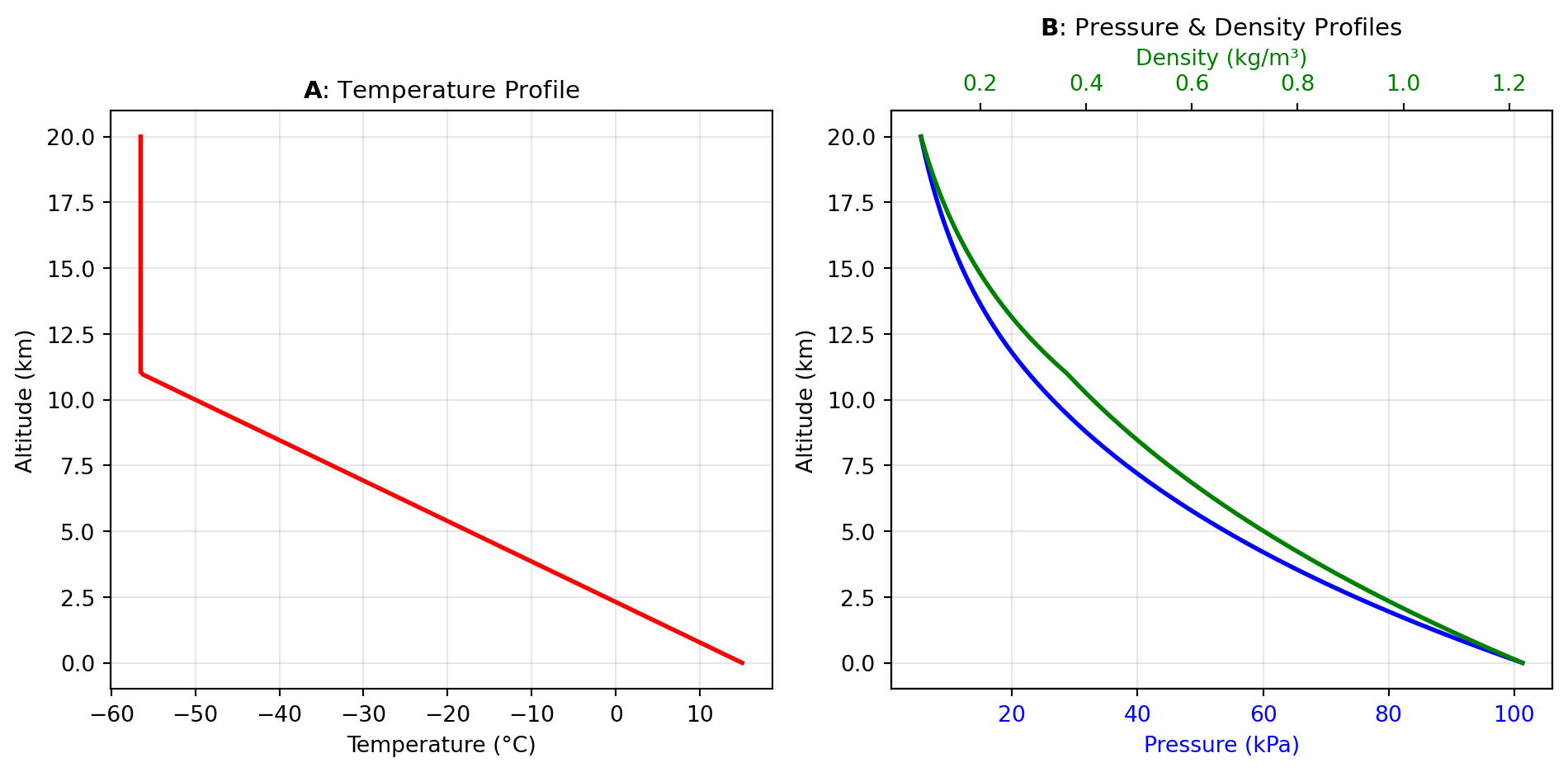
Standard Atmosphere Models like the US Standard Atmosphere 1976 provide baseline atmospheric properties as a function of altitude, assuming average mid-latitude conditions. The ATMOSPHERE_1976 tool implements this widely-used reference model, providing temperature, pressure, and density from sea level to 1000 km. These models divide the atmosphere into layers (troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere) with distinct temperature gradients, as shown in Figure 1.
Empirical Atmospheric Models like NRLMSISE-00 account for real-world variability including geographic location, time of day, solar activity, and geomagnetic conditions. The ATMOS_NRLMSISE00 tool uses this sophisticated model, particularly important for satellite operations where atmospheric drag varies significantly with solar cycles and geomagnetic storms. These models are implemented using Python libraries like NumPy for numerical computations.
Atmospheric Path Calculations determine the total mass of air along a line of sight through the atmosphere, critical for optical astronomy, remote sensing, and solar radiation modeling. The AIRMASS tool computes this quantity for any viewing angle and altitude, enabling corrections for atmospheric extinction and refraction effects.

Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| AIRMASS | Calculate the mass of air per square meter in the atmosphere along a given angle using a density profile. |
| ATMOS_NRLMSISE00 | Compute temperature, density, and pressure using the NRLMSISE-00 atmospheric model. |
| ATMOSPHERE_1976 | Calculate standard atmospheric properties at a given altitude using the US Standard Atmosphere 1976 model. |