Hypothesis Tests
Overview
Hypothesis testing is a formal statistical procedure used to determine whether an observed effect in data is real or likely due to random chance. It provides a structured framework for making evidence-based decisions about populations based on sample data. All hypothesis tests in this category are implemented using SciPy’s comprehensive statistical functions.
Fundamental Concepts
Every hypothesis test involves setting up competing claims about a population parameter:
- Null Hypothesis (H_0): The default assumption that there is no effect or no difference (e.g., “There is no difference between the groups” or “The variable has no association”).
- Alternative Hypothesis (H_1 or H_a): The claim you are testing for (e.g., “Group A differs from Group B” or “The variables are associated”).
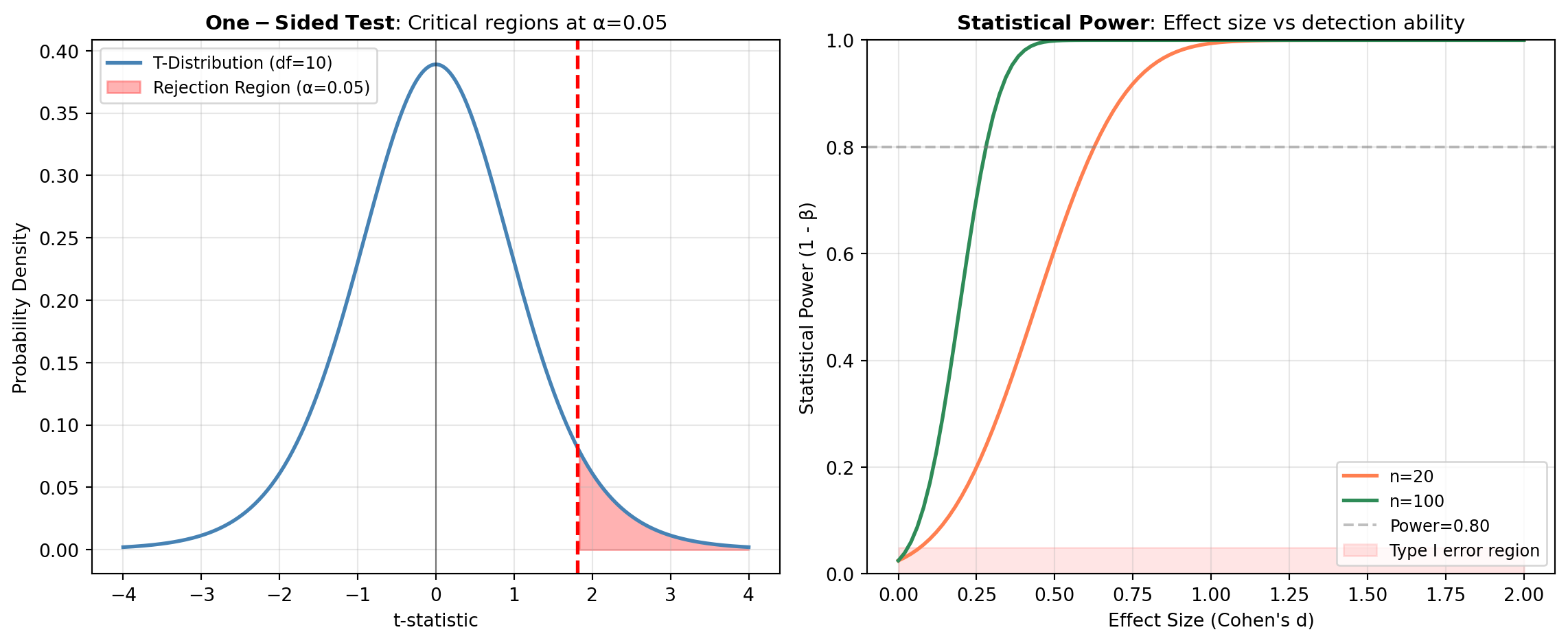
- P-value: The probability of observing results as extreme as or more extreme than those obtained, assuming the null hypothesis is true. When p < \alpha (typically 0.05), we reject H_0 in favor of H_1.
- Significance Level (\alpha): The threshold (usually 0.05) for deciding whether the p-value provides sufficient evidence against the null hypothesis.
- Type I and Type II Errors: Type I (false positive) occurs when rejecting a true H_0; Type II (false negative) occurs when failing to reject a false H_0.

Test Selection by Data Structure
Hypothesis tests are organized by the structure of your data and research question:
One Sample Tests: Used when testing a single sample against a population parameter or theoretical distribution. These include tests for the mean (e.g.,
TTEST_1SAMP), goodness-of-fit tests (e.g.,SHAPIRO,KSTEST), and tests for specific distributional properties (e.g.,NORMALTESTfor normality,JARQUE_BERAfor skewness and kurtosis).Independent Sample Tests: Used when comparing two or more independent groups or samples. These range from parametric tests assuming normality and equal variances (e.g.,
TTEST_IND,F_ONEWAY) to non-parametric alternatives (e.g.,MANNWHITNEYU,KRUSKAL) and specialized tests for variance equality (e.g.,LEVENE,FLIGNER). Multiple comparison corrections are supported through specialized tests likeDUNNETT.Association and Correlation Tests: Used when examining relationships between two or more variables. These include correlation-based tests (e.g.,
PEARSONR,SPEARMANR,KENDALLTAU) for measuring linear or monotonic associations, tests of independence for categorical variables (e.g.,CHI2_CONTINGENCY,FISHER_EXACT), and robust regression alternatives (e.g.,THEILSLOPES,SIEGELSLOPES) for estimating relationships while reducing the influence of outliers.
Choosing the Right Test
Your choice of test depends on several factors: the number of samples or groups, whether your data are independent or paired, the scale of measurement (continuous, ordinal, categorical), whether you want to assume normality and equal variances, and your research hypothesis (one-sided or two-sided). Parametric tests are generally more powerful when their assumptions are met, while non-parametric tests are more robust to violations of these assumptions but may have less power. Exact tests (e.g., FISHER_EXACT, BARNARD_EXACT) are particularly useful for small sample sizes or sparse contingency tables.
Association Correlation
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| BARNARD_EXACT | Perform Barnard’s exact test on a 2x2 contingency table. |
| BOSCHLOO_EXACT | Perform Boschloo’s exact test on a 2x2 contingency table. |
| CHI2_CONTINGENCY | Perform the chi-square test of independence for variables in a contingency table. |
| FISHER_EXACT | Perform Fisher’s exact test on a 2x2 contingency table. |
| KENDALLTAU | Calculate Kendall’s tau, a correlation measure for ordinal data. |
| PAGE_TREND_TEST | Perform Page’s L trend test for monotonic trends across treatments. |
| PEARSONR | Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient and p-value for two datasets. |
| POINTBISERIALR | Calculate a point biserial correlation coefficient and its p-value. |
| SIEGELSLOPES | Compute the Siegel repeated medians estimator for robust linear regression using scipy.stats.siegelslopes. |
| SOMERSD | Calculate Somers’ D, an asymmetric measure of ordinal association between two variables. |
| SPEARMANR | Calculate a Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient with associated p-value. |
| THEILSLOPES | Compute the Theil-Sen estimator for a set of points (robust linear regression). |
| WEIGHTEDTAU | Compute a weighted version of Kendall’s tau correlation coefficient. |
Independent Sample
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| ALEXANDERGOVERN | Performs the Alexander-Govern test for equality of means across multiple independent samples with possible heterogeneity of variance. |
| ANDERSON_KSAMP | Performs the k-sample Anderson-Darling test to determine if samples are drawn from the same population. |
| ANSARI | Performs the Ansari-Bradley test for equal scale parameters (non-parametric) using scipy.stats.ansari. |
| BRUNNERMUNZEL | Computes the Brunner-Munzel nonparametric test for two independent samples. |
| BWS_TEST | Performs the Baumgartner-Weiss-Schindler test on two independent samples. |
| CVM_2SAMP | Performs the two-sample Cramér-von Mises test using scipy.stats.cramervonmises_2samp. |
| DUNNETT | Performs Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons of means against a control group. |
| EPPS_SINGLE_2SAMP | Compute the Epps-Singleton test statistic and p-value for two samples. |
| F_ONEWAY | Performs a one-way ANOVA test for two or more independent samples. |
| FLIGNER | Performs the Fligner-Killeen test for equality of variances across multiple samples. |
| FRIEDMANCHISQUARE | Computes the Friedman test for repeated samples. |
| KRUSKAL | Computes the Kruskal-Wallis H-test for independent samples. |
| KS_2SAMP | Performs the two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit. |
| LEVENE | Performs the Levene test for equality of variances across multiple samples. |
| MANNWHITNEYU | Performs the Mann-Whitney U rank test on two independent samples using scipy.stats.mannwhitneyu. |
| MEDIAN_TEST | Performs Mood’s median test to determine if two or more independent samples come from populations with the same median. |
| MOOD | Perform Mood’s two-sample test for scale parameters. |
| POISSON_MEANS_TEST | Performs the Poisson means test (E-test) to compare the means of two Poisson distributions. |
| RANKSUMS | Computes the Wilcoxon rank-sum statistic and p-value for two independent samples. |
| TTEST_IND | Performs the independent two-sample t-test for the means of two groups. |
| TTEST_IND_STATS | Perform a t-test for means of two independent samples using summary statistics. |
One Sample
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| BINOMTEST | Perform a binomial test for the probability of success in a Bernoulli experiment. |
| JARQUE_BERA | Perform the Jarque-Bera goodness of fit test for normality. |
| KSTEST | Performs the one-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit. |
| KURTOSISTEST | Test whether the kurtosis of a sample is different from that of a normal distribution. |
| NORMALTEST | Test whether a sample differs from a normal distribution (omnibus test). |
| QUANTILE_TEST | Perform a quantile test to determine if a population quantile equals a hypothesized value. |
| SHAPIRO | Perform the Shapiro-Wilk test for normality. |
| SKEWTEST | Test whether the skewness of a sample is different from that of a normal distribution. |
| TTEST_1SAMP | Perform a one-sample t-test for the mean of a group of scores. |